Why Peanuts Are Actually Legumes, Not Nuts
Discover why peanuts are classified as legumes, not nuts. Learn the key differences between peanuts and tree nuts, their botanical classification, and what this means for your health.

Introduction
If you’ve ever wondered “are peanuts nuts or legumes?” you’re not alone. Despite their misleading name and similar nutritional profile to tree nuts, peanuts belong to an entirely different plant family.
In fact, these popular snacks have more in common with peas than with almonds or walnuts. Let’s crack open this fascinating topic and explore the true nature of peanuts.
The Basic Classification
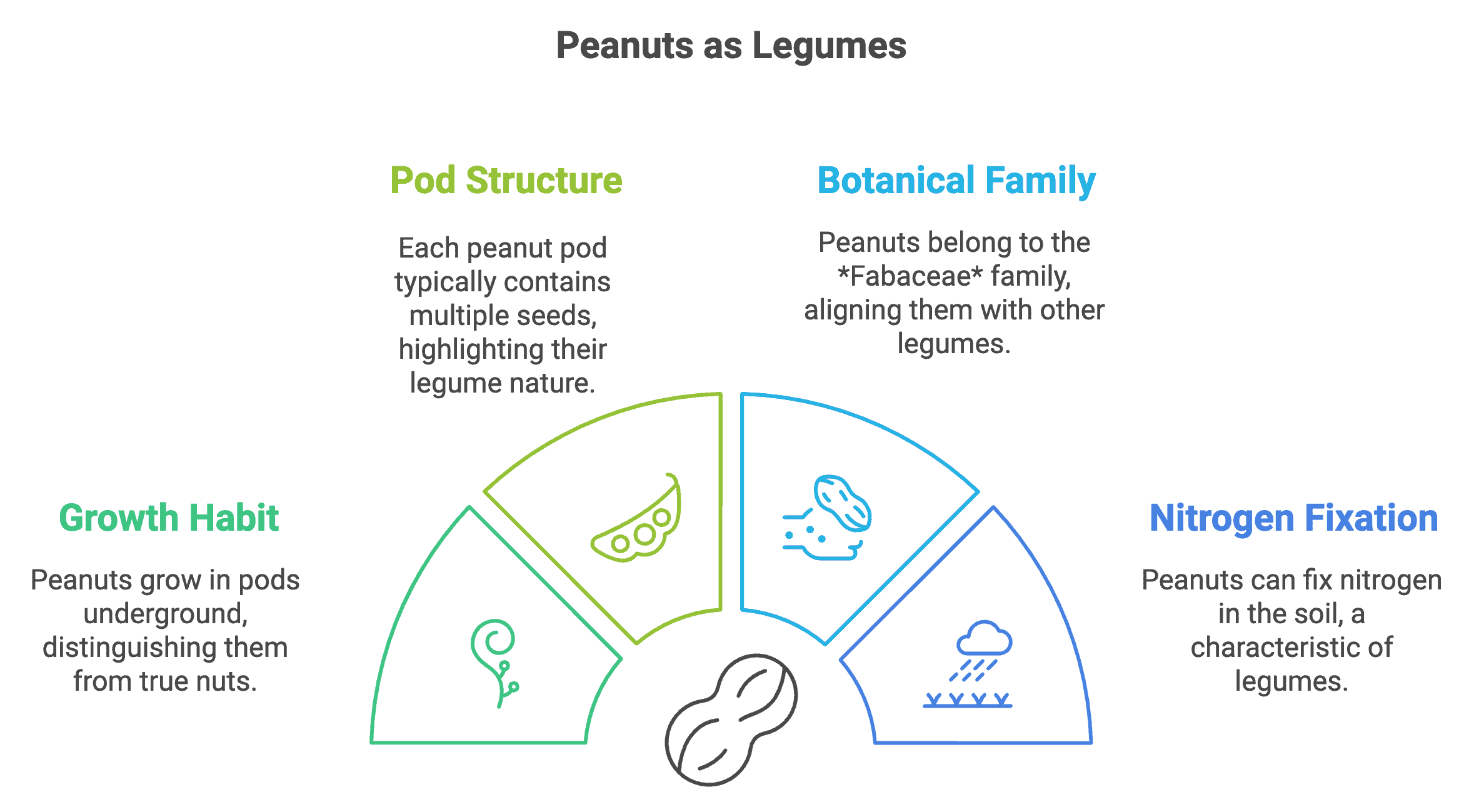
Peanuts (Arachis hypogaea) are officially classified as legumes, placing them in the same family as peas, lentils, and beans.
Unlike true nuts, which grow on trees, peanuts are legumes that grow underground. This classification isn’t just a botanical technicality – it reveals important differences in how these plants grow, develop, and provide nutrition.

Key differences that make peanuts legumes:
- They grow in pods underground, not on trees
- Each pod typically contains multiple seeds (peanuts)
- They’re part of the Fabaceae (or Leguminosae) family
- They can fix nitrogen in the soil, like other legumes
Botanical Differences
The growing process of peanuts is particularly fascinating and sets them apart from true nuts. Here’s how peanuts develop:
- The peanut plant first produces yellow flowers above ground
- After pollination, the flower stems (called pegs) grow downward
- These pegs push into the soil
- The peanut pods develop and mature underground
This unique growing process is completely different from tree nuts, which develop their fruits on branches.
So when someone asks, “do peanuts come from peas?” the answer is no – but they are botanical cousins, sharing the legume family’s characteristic of producing seeds in pods.
The Legume Family Connection
Are peas and peanuts related? Yes, they’re both members of the legume family, sharing several important characteristics:
Common legume family traits:
- Pod-based seed development
- Nitrogen-fixing root nodules
- Similar protein structures
- Comparable plant growth patterns
Unlike the common misconception that peanuts are dried peas, they’re distinct plants within the same family, each with unique characteristics and nutritional profiles.

Health Implications of Classification
Understanding that peanuts are legumes rather than nuts has important health implications:
Allergies:
- Peanut allergies are distinct from tree nut allergies
- Some people allergic to peanuts can safely eat tree nuts (and vice versa)
- Always consult an allergist for specific guidance
Nutritional Benefits:
- High in plant-based protein
- Rich in healthy fats
- Good source of fiber
- Contains beneficial compounds typical of legumes
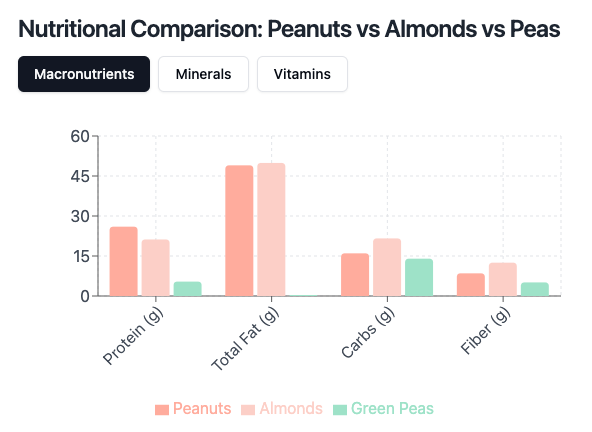
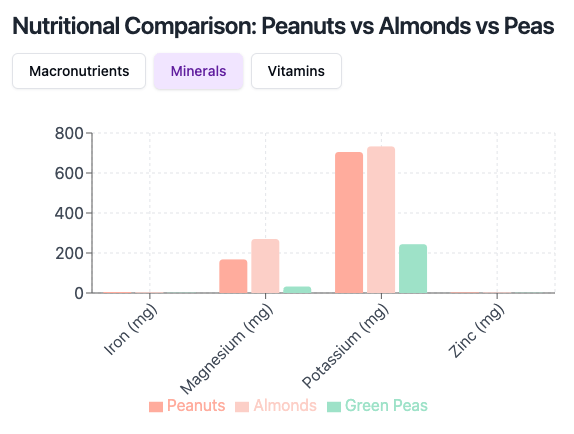
Nutritional Comparison
Peanuts vs Almonds vs Peas – Macronutrients
Peanuts vs Almonds vs Peas – Minerals
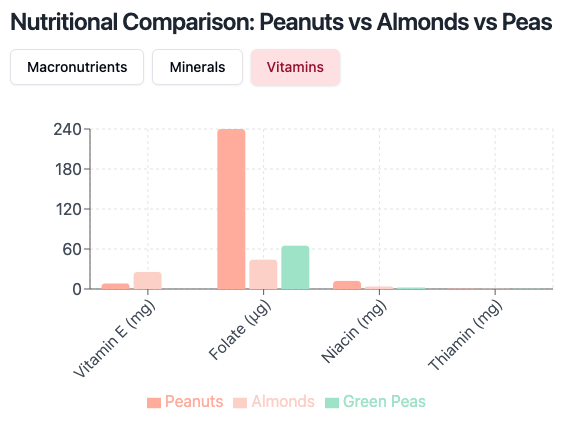
Peanuts vs Almonds vs Peas – Vitamins
Common Questions Answered (FAQ)
Conclusion
While peanuts might share some nutritional similarities with tree nuts, they are firmly classified as legumes. This unique classification gives them special properties and benefits that set them apart from both tree nuts and other legumes.
Understanding this distinction can help you make more informed decisions about your diet and nutrition.
Discover more from The Kitchen Code
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







